Gin - 参数绑定到结构体
绑定到结构体
Go 的结构体支持通过标签(tag) 定义解析规则,Gin 框架会依据这些标签自动完成请求数据到结构体的绑定。例如 Name string "form:name" 会指定该字段对应请求中的 name 参数(不同绑定类型对 tag 的解析逻辑有差异,后续会详细说明)。
Gin 中核心绑定方法分为两大类别:ctx.Bind 系列和 ctx.ShouldBind 系列,它们的核心差异在于输入无效时的处理逻辑:
Bind系列:输入数据无效(如类型不匹配、必填项缺失)时,会自动返回400 Bad Request响应,并设置响应头Content-Type: text/plain,同时中止后续处理;ShouldBind系列:仅返回绑定错误,不会主动修改响应状态码,也不会中止请求流程,需开发者自行处理错误逻辑。
两大类别下还提供了精准绑定方法,用于指定具体的数据来源,例如:
BindJSON/ShouldBindJSON:仅解析请求体中的 JSON 数据;BindXML/ShouldBindXML:仅解析请求体中的 XML 数据;BindForm/ShouldBindForm:仅解析表单(application/x-www-form-urlencoded)或查询参数(Query String);- 其他:
BindYAML、BindTOML等,对应不同数据格式。
通用结构体绑定(适配 GET/POST 多请求类型)
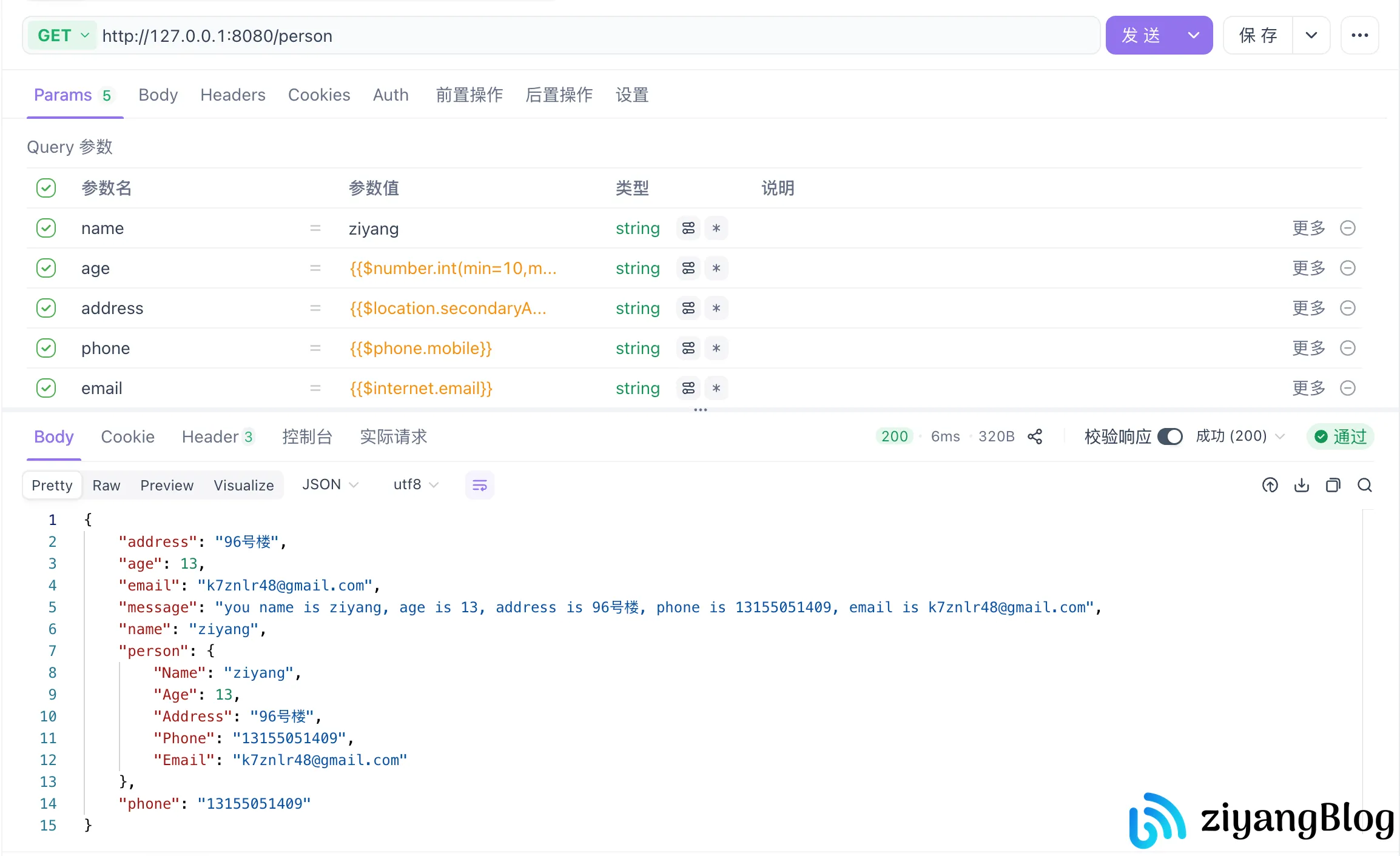
如果需要让同一个结构体适配 GET 请求(参数在 URL 查询串)和 POST 请求(参数在表单或 JSON 体),推荐使用 form 标签定义结构体——因为 GET 请求的参数只能通过 form 标签绑定,而 ShouldBind 会自动根据请求头 Content-Type 适配 POST 数据格式(表单/JSON 均可)。
完整代码示例
1 | |
请求示例
1. GET 请求(参数在 URL 查询串)
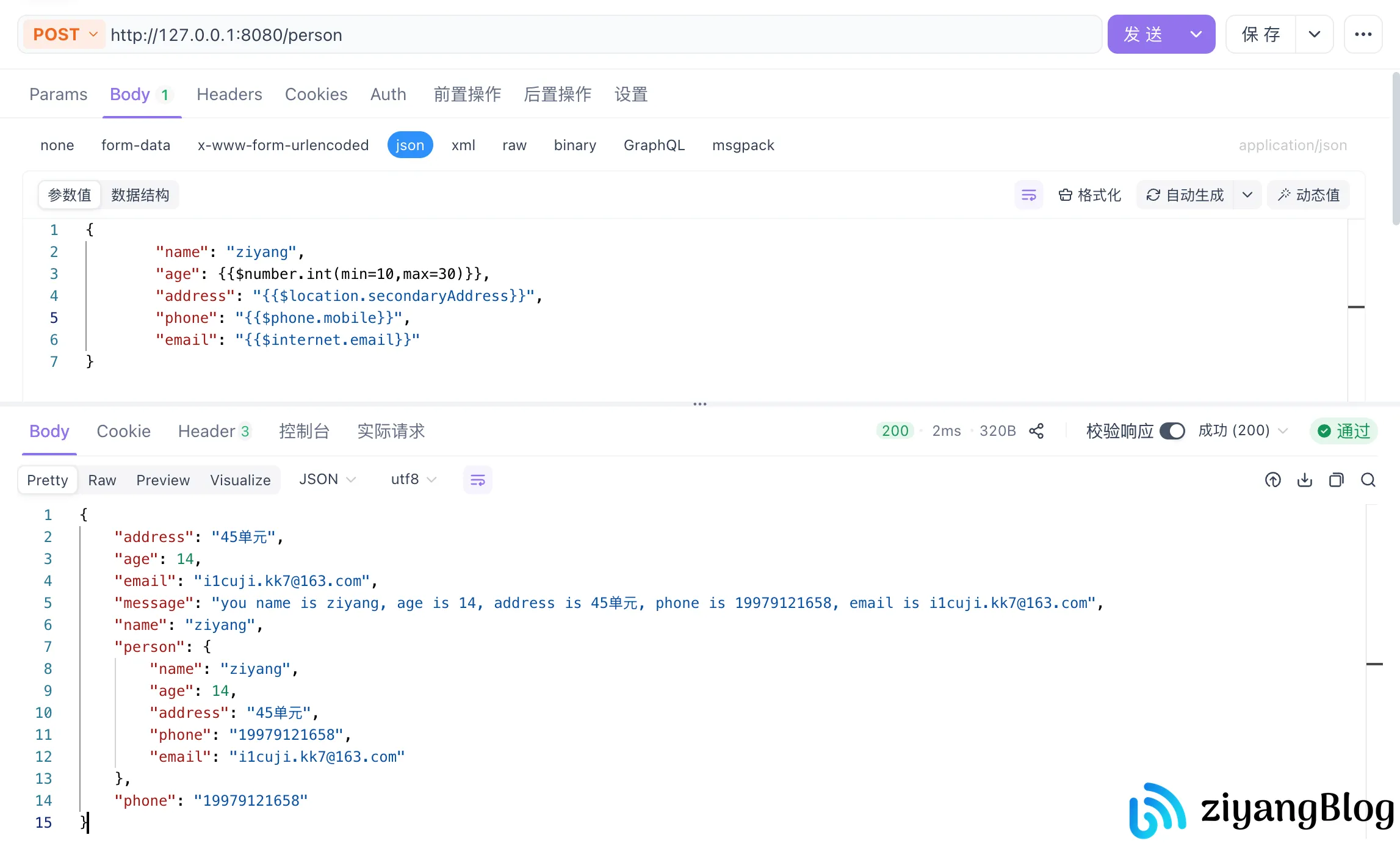
2. POST 请求(JSON 格式请求体)
核心原理(源码视角)
ShouldBind 之所以能适配多种请求类型,是因为它会先根据请求头 Content-Type 判断数据格式,再调用对应的解析逻辑:
- JSON 解析(ShouldBindJSON):忽略结构体的
form标签,直接通过字段名(大小写敏感)匹配 JSON 键名(如结构体Name对应 JSON 的Name或name,Gin 内部做了大小写兼容); - 表单/查询串解析(ShouldBindForm):严格依赖
form标签,通过field.Tag.Get("form")获取绑定的参数名,再通过反射将请求参数赋值给结构体字段; - 其他格式(XML/YAML 等):逻辑与 JSON 类似,忽略
form标签,按字段名匹配。
关键源码片段说明:
BindJSON:直接解析请求体为 JSON,不依赖form标签;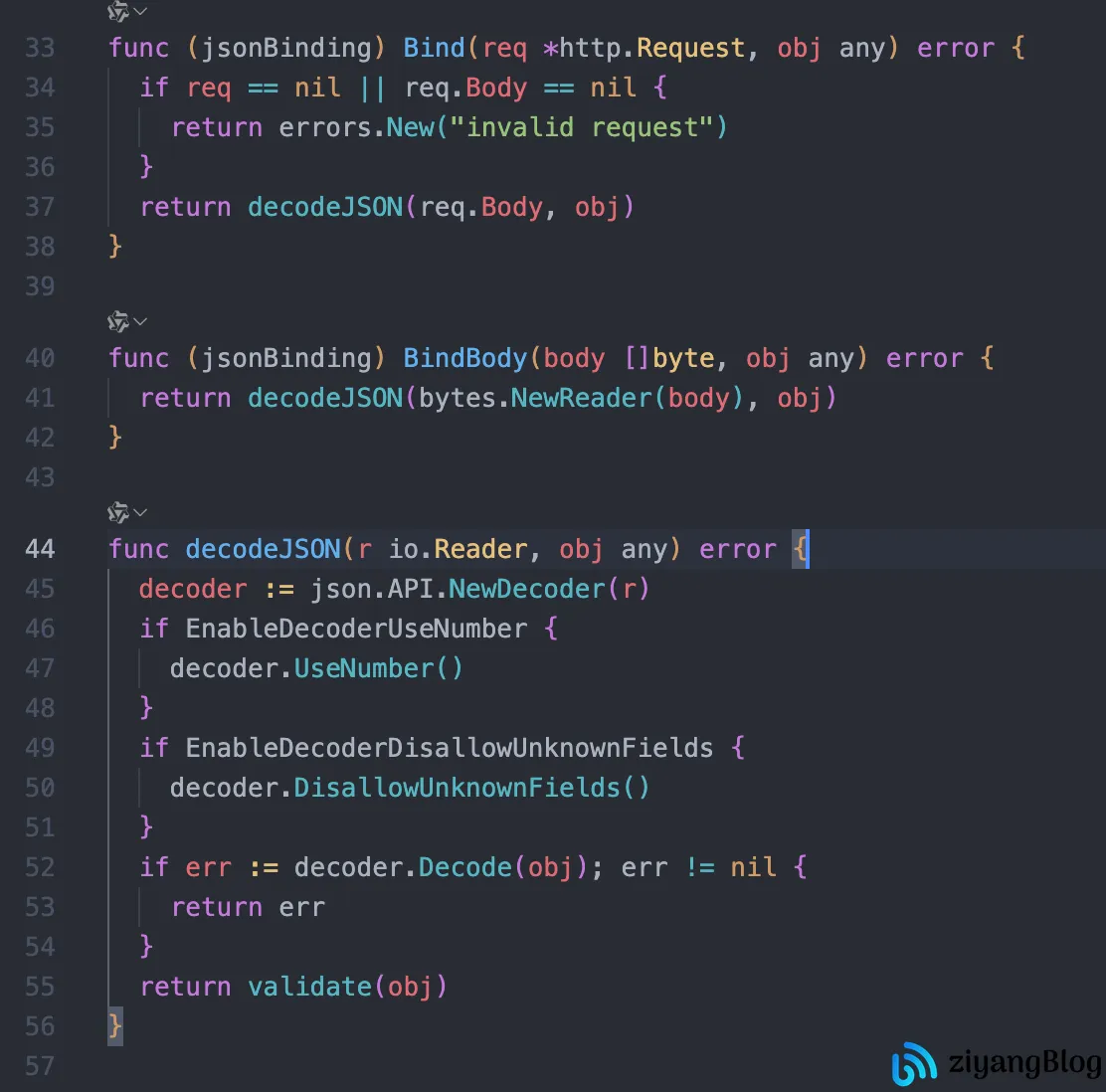
BindForm:调用mapForm方法,通过反射读取form标签,匹配请求参数;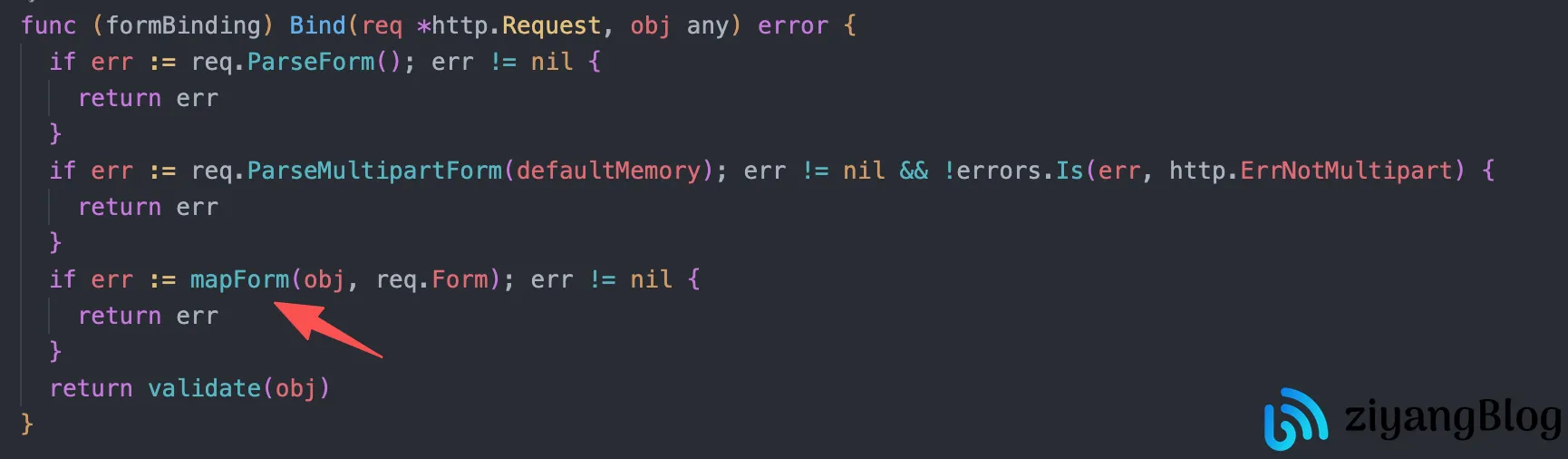
mapForm:调用mapFormByTag,通过反射遍历结构体字段;
mappingByPtr/mapping:核心反射逻辑,通过field.Tag.Get(tag)提取form标签对应的参数名(如field.Tag.Get("form")从form:name中获取name),再从请求中提取值并转换类型。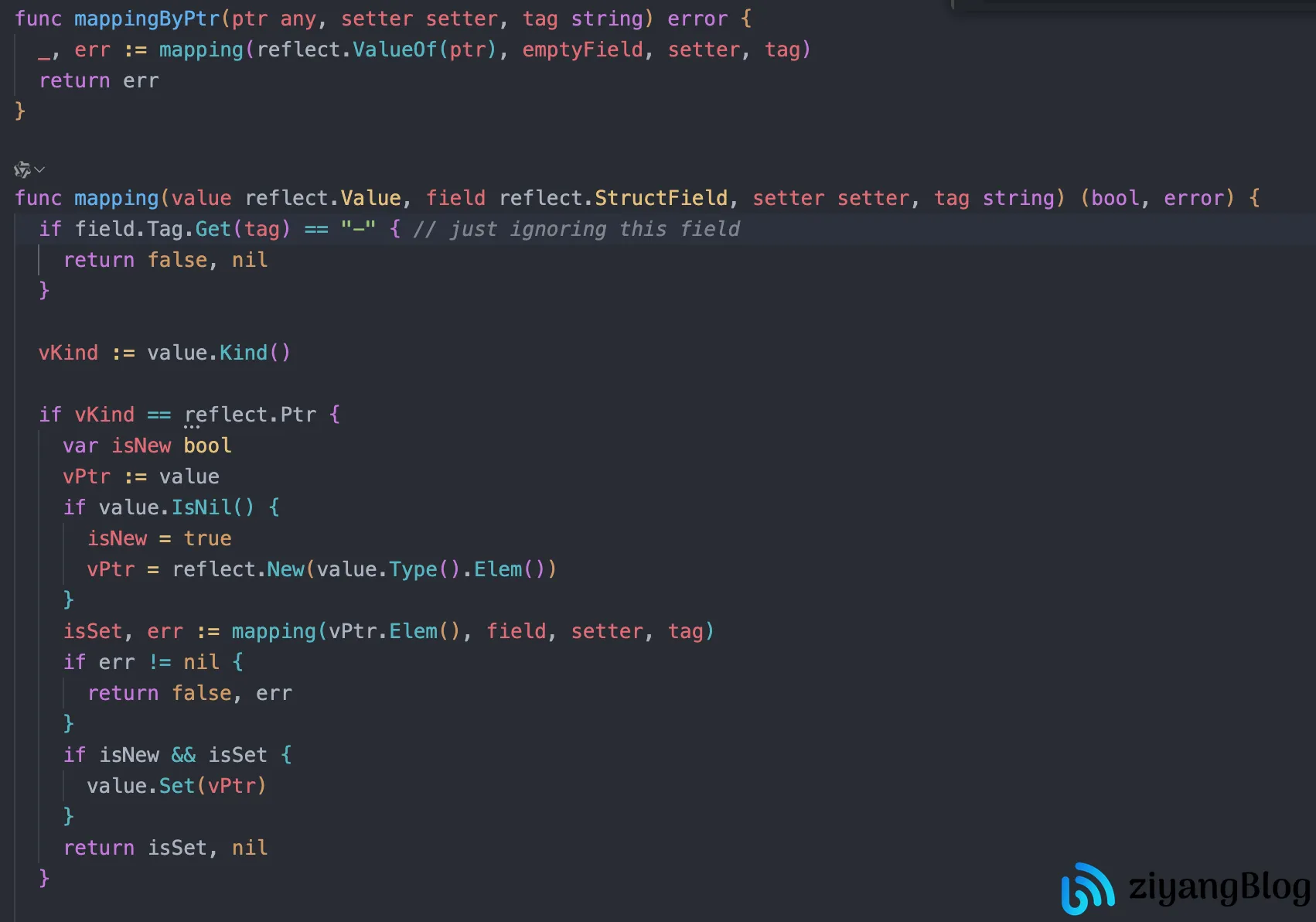
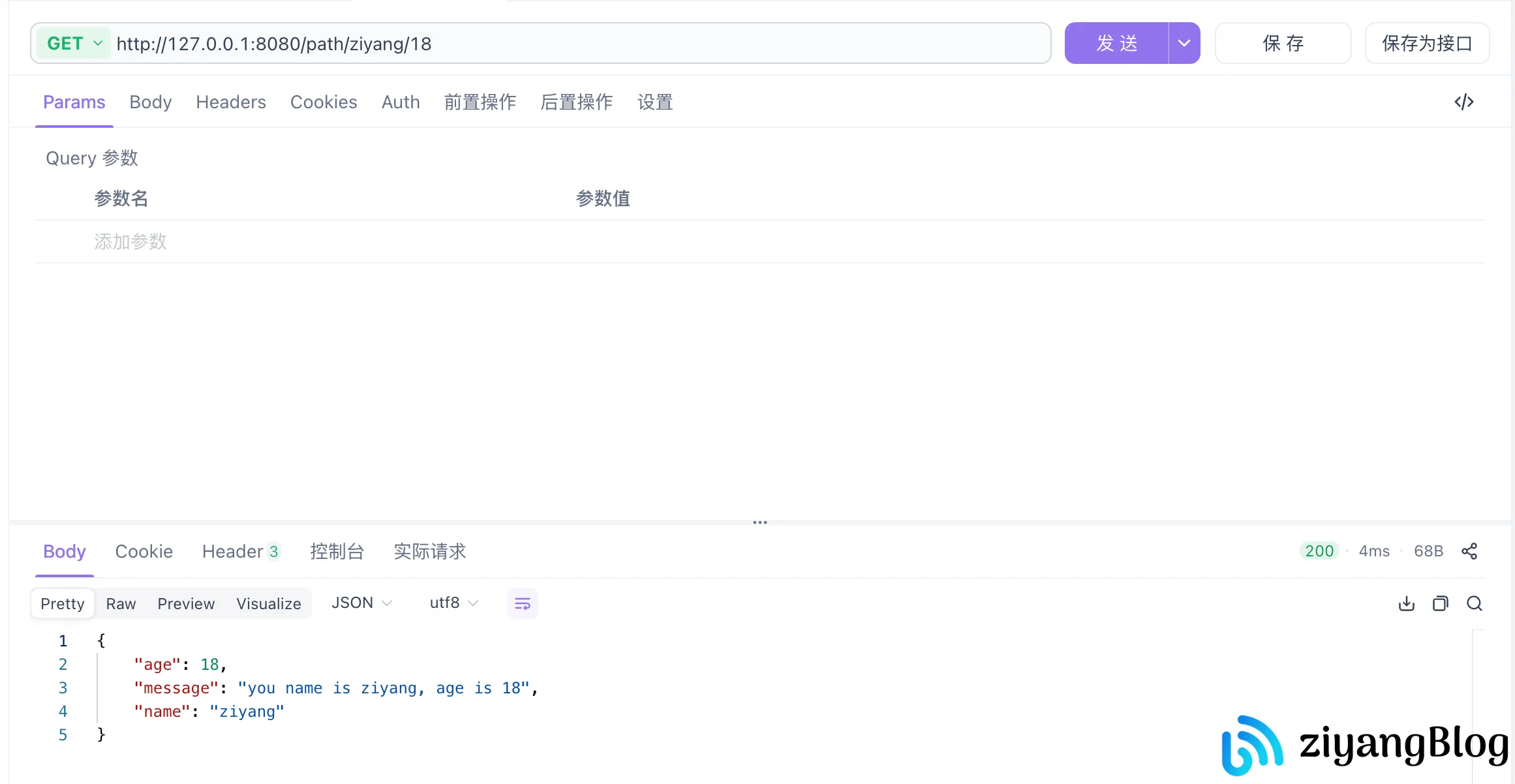
特殊绑定:从 URL 路径绑定(BindURI)
大部分绑定方法(如 BindJSON、BindForm)都是 Bind/ShouldBind 的快捷别名,最终都通过统一逻辑处理,但 BindURI(ShouldBindUri)是特例——它专门用于从 URL 路径参数(而非查询串)绑定数据,且必须使用 uri 标签定义结构体。
代码示例
1 | |
请求示例
Gin - 参数绑定到结构体
https://blog.pangcy.cn/2025/11/21/后端编程相关/go/gin/Gin - 参数绑定到结构体/